 |
Langley Research CenterTurbulence Modeling Resource |
DNS: 2-D Turbulent Separation Bubbles
Return to: Data from DNS - Intro Page
Return to: Turbulence Modeling Resource Home PageThe data on this page were provided by G. Coleman.
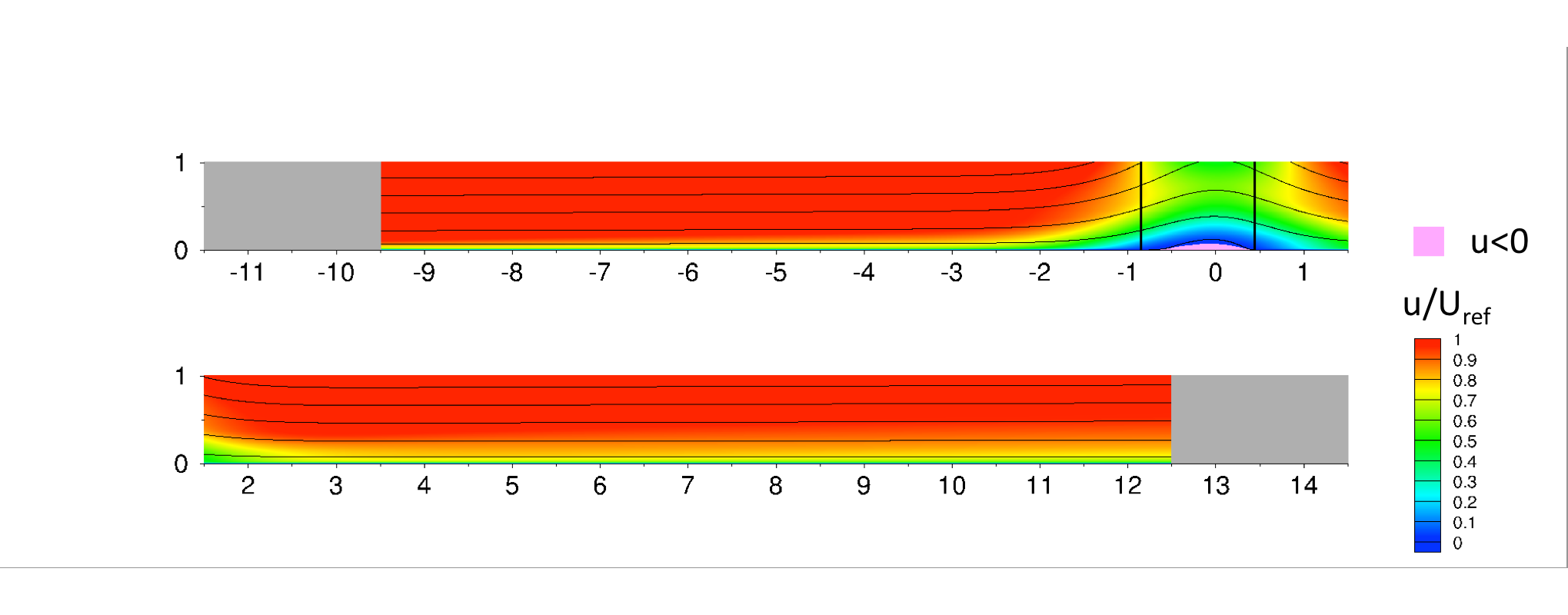
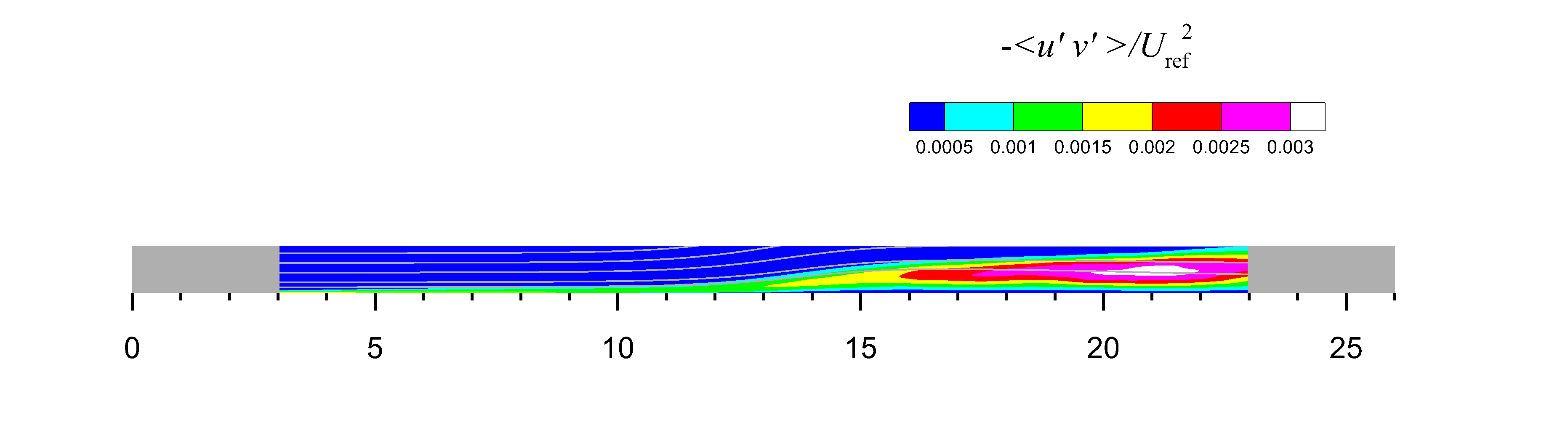
Suction and Blowing on Top Wall
This flow is a 2-D
separation bubble, with the separation and reattachment forced by velocity transpiration (suction and blowing)
along the top boundary. The oncoming boundary layer in the zero-pressure-gradient region has a
Re_theta of around 2000. The flow was computed
using the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations in a pseudo-spectral code.
Additional details concerning the data,
code, and computational methodology can be found in:
See also the related page:
DNS: Swept Turbulent Separation Bubble.
Here is an explanation of what is in the data files provided:
The DNS data files for the main case (Case C)
from the abovementioned paper are given here:
DNS data at other conditions in the paper are given below:
Suction Only on Top Wall
This flow is very similar to
the above, except that the top-wall velocity transpiration is suction only, so that the adverse
pressure gradient is not followed by a favorable pressure gradient in this case.
Additional details can be found in:
Here is an explanation of what is in the data files provided:
The DNS data files for the main case (Case E) are provided here:
DNS data at other conditions in the paper are given below:
Return to: Data from DNS - Intro Page
Recent significant updates: Responsible NASA Official:
Ethan Vogel
12/18/2023 - added field data for cases A and B
01/08/2022 - updated NASA/TM-20210020762 (errata)
10/18/2021 - added suction-only cases
08/12/2020 - revised README file to v7 (gives more precise values for Vmax to impose top-wall transpiration profile)
02/19/2019 - added cases A and B
06/01/2018 - added results with average in x, renamed unaveraged files, updated README file
Page Curator:
Clark Pederson
Last Updated: 12/18/2023